WA’s largest export canola markets in 2021/22 were Germany, Japan, UAE, Belgium, France, and the Netherlands. WA canola is renowned for its high oil content – with the state often achieving higher oil contents than the rest of the nation.
Western Australian canola industry
Canola is an important crop in Western Australia, with average yearly production over the last 5 years estimated at 2.2 million tonnes, worth around $1.2 billion to the state economy each year. Nearly all WA canola production is exported, mostly into Asia for human use and to Europe for biofuel production.
The department has a strong canola research, development, and extension program with a focus on developing profitable agronomic packages and overcoming pest and disease constraints.

Canola is Western Australia's third largest broadacre crop after wheat and barley, with production estimated at over 2.5 million tonnes in 2023-24.
Production
Canola is Western Australia's third largest broadacre crop after wheat and barley with production estimated at over 2.5 million tonnes in 2023-24.
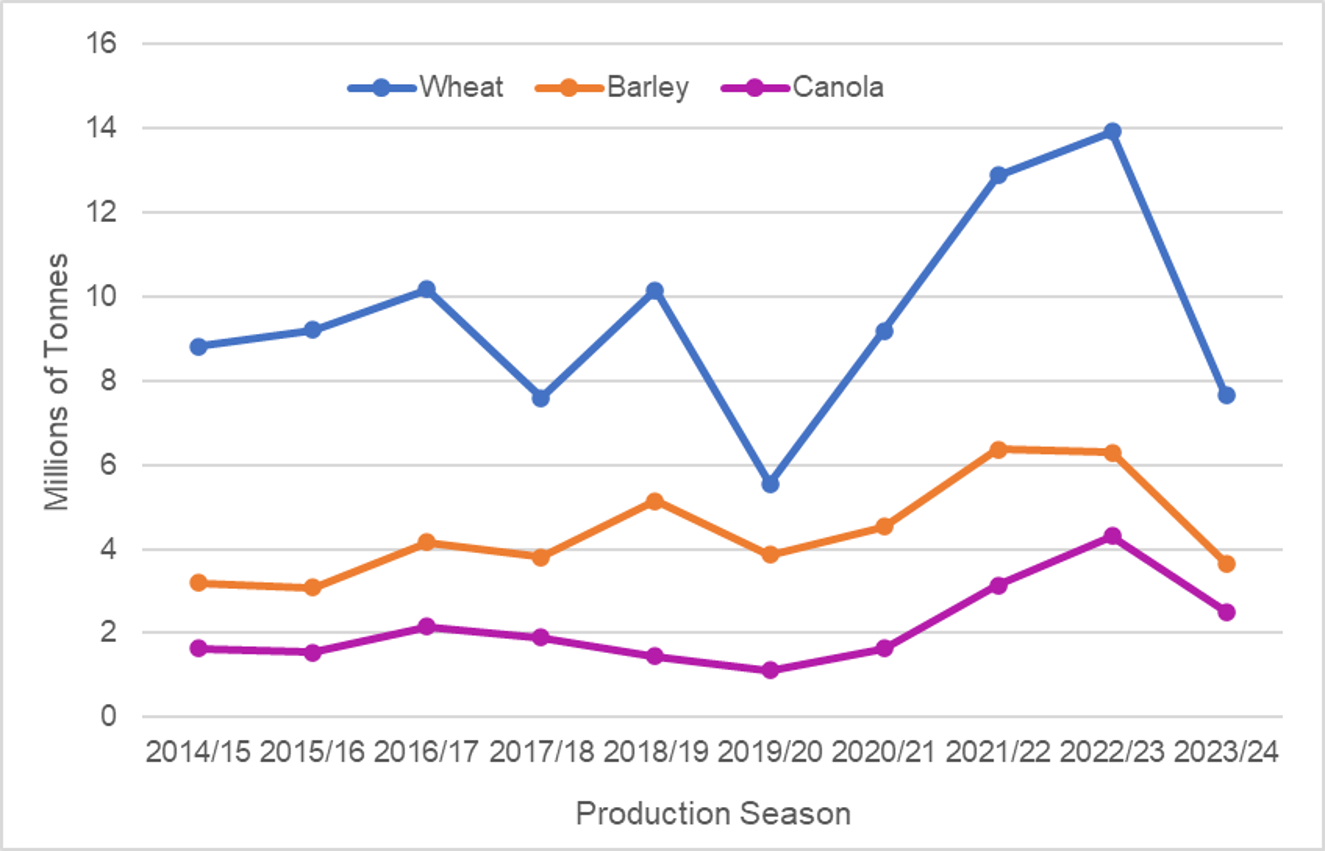
Wheat, barley, and canola production in Western Australia
WA is the dominant Australian state for canola production, accounting for more than 50% of the nation's 5-year average annual production of 4 million tonnes.
As well as being profitable, canola has become the most important break crop in WA cereal production systems, overtaking lupin due to higher profitability and better weed control options.
WA canola is grown using sustainable farming systems that can be certified to meet the sustainability criteria required to access the European Union markets.
Both conventional and genetically modified canola varieties are grown in WA, with strict segregation in the supply chain allowing the two systems to co-exist.
Exports
WA exports 90% of the canola it produces, accounting for over half of the nation's total canola exports. The value of WA canola exports has been increasing strongly since 2000 and is running at a five-year average of around $1.2 billion per year.
The major markets for WA canola in 2022 were the European Union (EU), followed by Japan and United Arab Emirates (UAE). Canola is used for both production of biodiesel and food in the EU. Canola is also processed locally, and exported as canola oil to Taiwan, Japan, China, and Vietnam.
Processing
There are two local canola crushing operations, located at Pinjarra and Kojonup. Both are small by international industry standards. Between the two local crushers, about 60,000 tonnes of canola seed are processed per year, representing less than 5% of the state’s total canola production.
Crop Sowing Guide
The Western Australian crop sowing guide is a one stop shop for information on all the major crops grown in Western Australia, compiled by the department. This edition includes the major crops grown in WA – wheat, barley, canola, oat, lupins, and pulses. The guide aims to provide information to support growers with decisions on the best choice of variety for each of the major crops for the upcoming season.
View the current Crop Sowing GuideDiseases and pests of canola
When selecting a canola variety for your cropping program, it is important to be aware of the variety's disease and pest package to allow for appropriate planning and proactive management to reduce risk of yield losses.
The severity of disease in canola crops depends on the presence of inoculum carried over from last season, favourability of seasonal conditions, pathotype virulence, and varietal susceptibility.
An annual review of your crop’s disease and pest resistance ratings is vital, as risk profiles change with the introduction of new pathotypes. Refer to the Herbicide tolerance, harvest maturity, oil content, blackleg rating and commercial information of current canola varieties in the Western Australian crop sowing guide below.
A rapidly developing issue for the Australian grains industry is development of fungicide resistance in a range of canola pathogens. Using a good Integrated Disease Management (IDM) approach can help reduce reliance on fungicides for disease management. More information on fungicide resistance is available from the Australian Fungicide Resistance Extension Network.
Pest insects and nematodes can have adverse and damaging impacts on agricultural production and market access, the natural environment, and our lifestyle.
Western Australia is free from some of the world's major pest insects. Biosecurity measures on your property are vital in preventing the spread of insect pests.
The department provides:
- biosecurity/quarantine measures at the WA border to prevent the entry of pest insects
- where relevant post border biosecurity measures
- advice on widespread pest insects present in the state
Disease symptoms, background, diagnosis, factors favouring risk and spread, yield and quality losses, and integrated management strategies are provided for the following diseases of canola:
More information
- Blackleg and its management in canola
- Blackleg spore maturity forecast for Western Australia
- Sclerotinia stem rot and its management in canola
- Turnip yellows virus and its management in canola
- Blackleg CM tool - Reduce blackleg crown canker disease
- Sclerotinia CM tool - Reduce sclerotinia stem rot
- UCI BlacklegCM tool - Manage blackleg upper canopy infections
Soil-borne pathogens and nematode pests infect plant roots and impact their ability to take up water and nutrients. Environmental factors such as soil moisture, temperature and nutrient availability will determine the severity of disease development. Soil-borne diseases and nematode pests are best managed by identifying the pathogens or pests causing plant decline, using crop and variety rotation, and chemical management, if available.
Nematode pests
Nematodes are microscopic, worm-like animals that feed on plant roots causing damage and yield loss in susceptible crops. Crops infested with plant parasitic nematodes are more susceptible to infection by fungal diseases such as rhizoctonia root rot.
More information
Pest symptoms, background, diagnosis, factors favouring risk and spread, yield and quality losses, and integrated pest management strategies are provided for the following pests of canola:
- Cutworms
- Diamondback moth
- European earwig
- False wireworm - bronzed field beetle larvae
- Lucerne flea
- Pest slugs and snails and their management in broadacre crops
- Rutherglen bug
Aphids
- Cabbage aphid
- Green peach aphid
- Turnip aphid
Mites
- Balaustium mite
- Clover mite (Bryobia mite)
- Redlegged earth mite
Native budworms
Snails
- Small conical snails
- Vineyard snail
- White Italian snail
Slugs
- Black keeled slug
- Reticulated slug
Weevils
- Desiantha weevil
- Fuller’s rose weevil
- Small lucerne weevil
- Vegetable weevil
Contact Us
Related links
- Canola - essentials for growing a successful crop
- Estimating the size of retained canola seed
- Canola seeding rate calculator
- Calculating canola seeding rate and recording sheet
- Canola agronomy research in Western Australia
- Registered fungicides for broadacre crops
- Crop Science and Grain Production research projects
- Subscribe to the Grains Convo Newsletter

