Three-horned bedstraw is widespread but relatively uncommon on cultivated land and other disturbed areas in temperate parts of the world and is a major weed of crops in parts of southeast Australia. In Australia, it is mainly found in paddocks that have been cropped for years. The weed is worse in areas that have pulse crops incorporated in the rotation.
The Grain, Seeds and Hay Industry Funding Scheme, funded by WA grain grower contributions, raises funds to address priority biosecurity threats specific to the WA grains, seeds and hay industries.
Bedstraw is a high priority eradication target for Western Australia. Report the presence of this pest.

Report three-horned bedstraw detections
Report suspected detections of three-horned bedstraw to either:
- Pest and Disease Information Service (PaDIS)
+61 8 9368 3080 | Email padis@dpird.wa.gov.au - MyPestGuide Reporter app or online tool.
Why three-horned bedstraw is a threat to WA
- Bedstraw is a competitive climbing plant that can form dense tangled clumps in crops. Effective herbicides exist for the weed in cereal crops and grass pastures, but it is more difficult to control bedstraw in canola, pulses, and legume-based pastures.
- The size of the seed makes it difficult to separate from canola during seed cleaning. Small, hooked stems on the seed make it difficult to remove from other crops using conventional seed cleaning equipment.
- At high densities, bedstraw can cause considerable yield loss in crops.
- Seeds contaminate grain and fodder. Seeds normally survive in the soil for 3 to 5 years but can survive longer in non-wetting soils.
- Known host to the stem nematode, Ditylenchus dipsaci.
- Three-horned bedstraw is spread by seed and can be dispersed by wind, water, on the plant, or by people or animals. In WA, most spread appears to be by movement in grain or agricultural machinery, particularly harvesters.
- To date bedstraw has only been recorded on a few farms in the central and great southern grain growing regions of WA, and eradication programs have been successful.
- Currently (October 2024), there is only one infested site under the eradication program in WA, and it is close to being eradicated.
- It mainly occurs on alkaline soils with annual rainfall from 300 to 550 mm but may grow under less favourable conditions and on other soil types.
More information
Legal status - Declared Pest, Prohibited - s12
Prohibited organisms are declared pests and may only be imported and kept subject to permits. Permit conditions applicable to some species may only be appropriate or available to research organisations or similarly secure institutions.
Status - C2 - Eradication / Prohibited
Present in WA - should be eradicated from part or all Western Australia.
What does ‘declared pest’ mean for you?
Bedstraw is a declared pest in WA. Information on the areas in which three-horned bedstraw is declared, and the requirements under the C2 ‘Eradication’ category to which it has been assigned, is available on the online tool, Western Australian Organism List (WAOL), located on the department website at dpird.wa.gov.au. Search for three-horned bedstraw in the WAOL using the scientific name Galium tricornutum.
What you need to do if bedstraw is found on the property you own/occupy
Bedstraw is subject to an eradication plan in WA. Each infested property will have a specific approved program detailing all eradication activities. Approved programs have comprehensive funding support from the Grains, Seeds and Hay Industry Funding Scheme. The Bedstraw Eradication Plan has been shown to be very effective in eradicating Bedstraw.
For details of approved programs and control support for landowners and occupiers to eradicate bedstraw, contact the department’s Bedstraw Project Manager (contact information under Contact us).
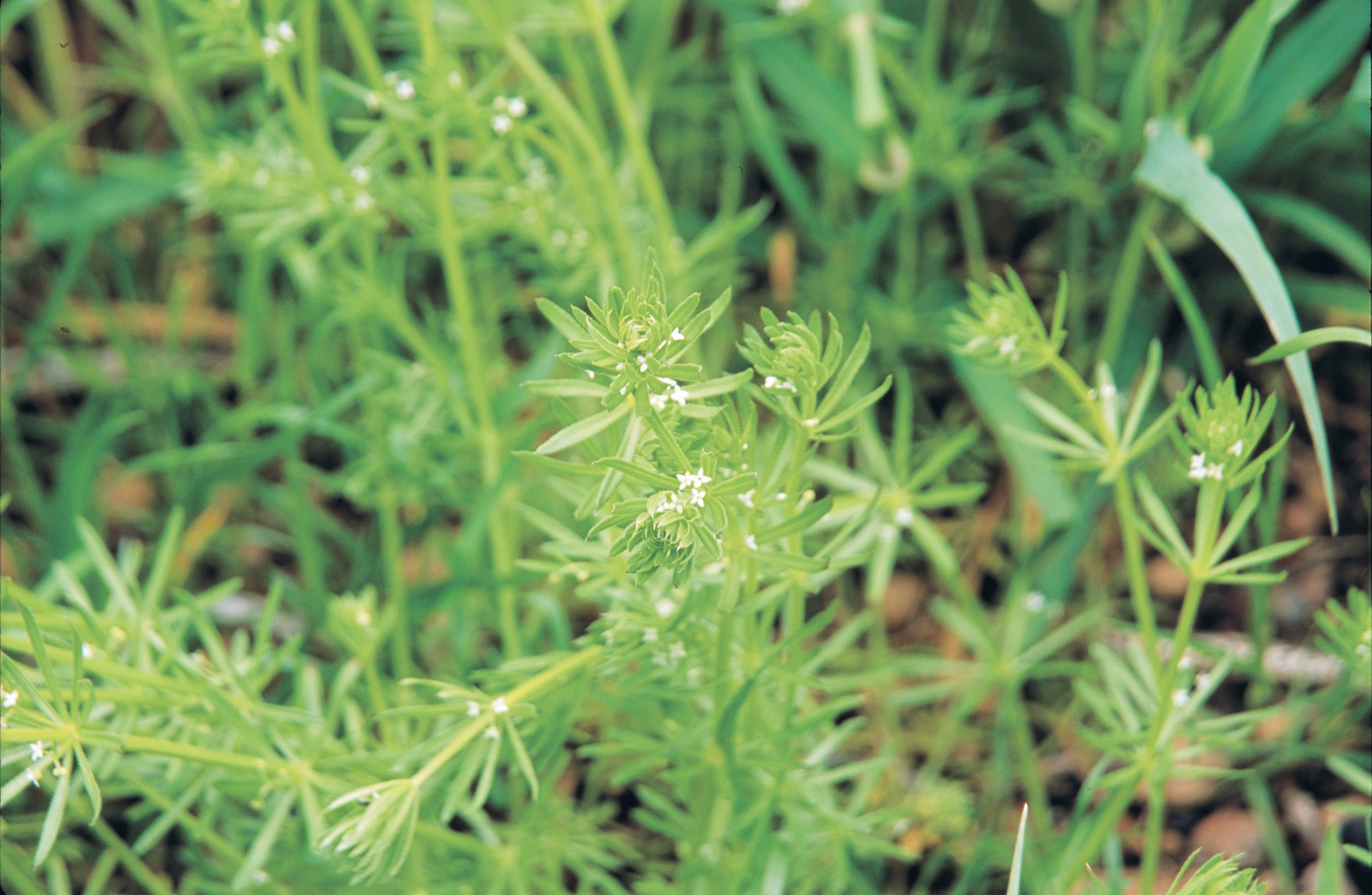
Three-horned bedstraw plants are straggly, scrambling or climbing, with weak branched stems up to 1.5m long. The whole plant feels sticky, caused by the leaves and stems being covered with tiny, hooked prickles.
Stems
- square when cut in cross-section with ridges at the corners and often hollow
- sprawling stems usually 50 centimetres (cm) long to up to 1 metre (m) long
- covered with downwardly pointing prickles, especially along the ribs.
Leaves
- long, narrow flat leaves formed in spirals of 6 to 8 at nodes on the stems
- no leafstalk (sessile)
- covered with hooked hairs on the upper leaf surface and tiny backward pointing prickles on the margins and on the underside midrib.

Flowers
- small (about 2 mm in diameter) and white, with 4 white petals
- carried on short, branched stems arising from the leaf spiral
- each flower is attached to a small stalk (pedicel) that is initially straight but becomes curved as the fruit forms
- groups of 3 flowers are attached to a straight stalk (peduncle) that is attached to the stem at the leaf axil or the end of the stem.
- Both pedicel and peduncle have tiny backward pointing prickles.

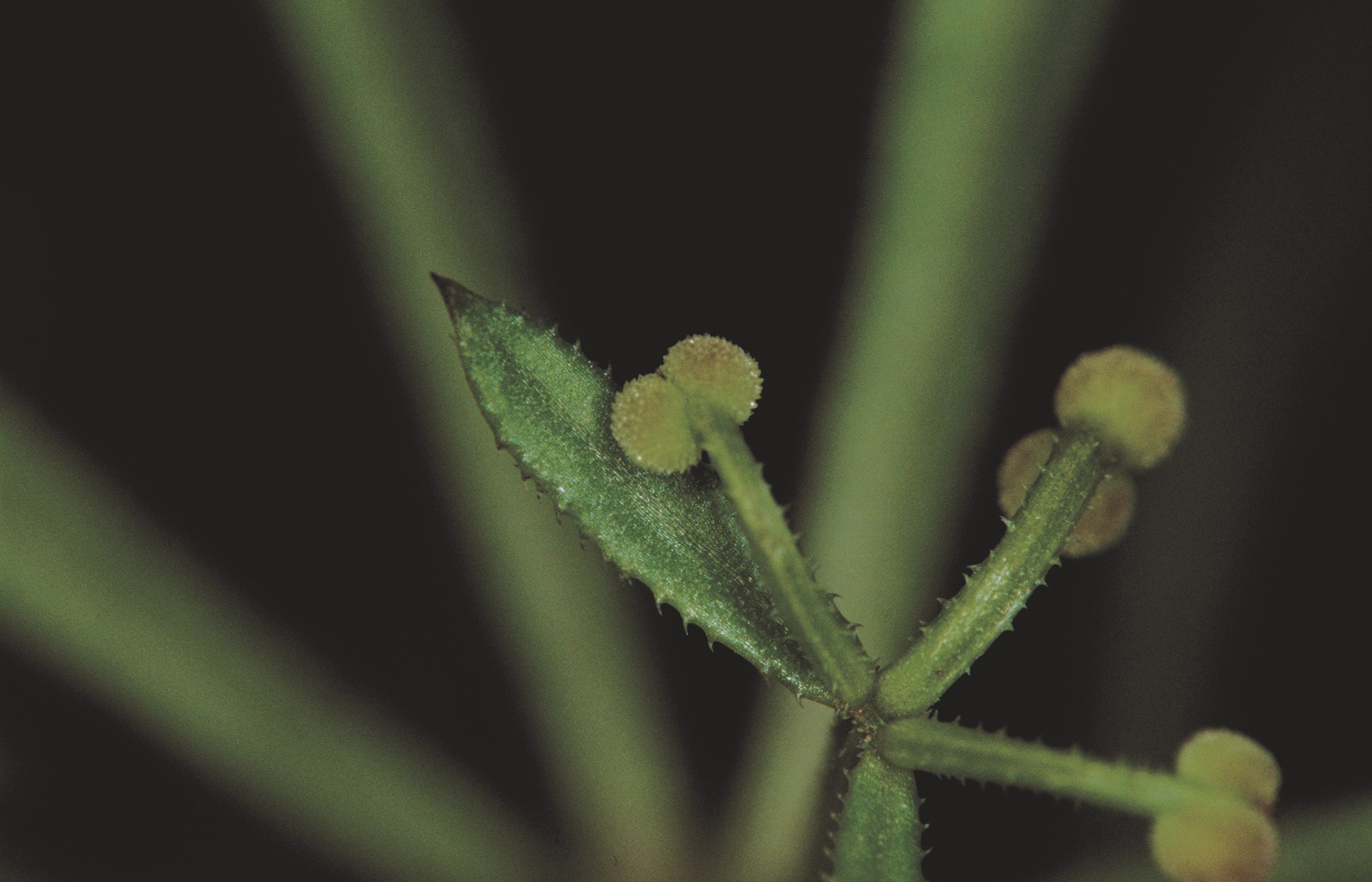
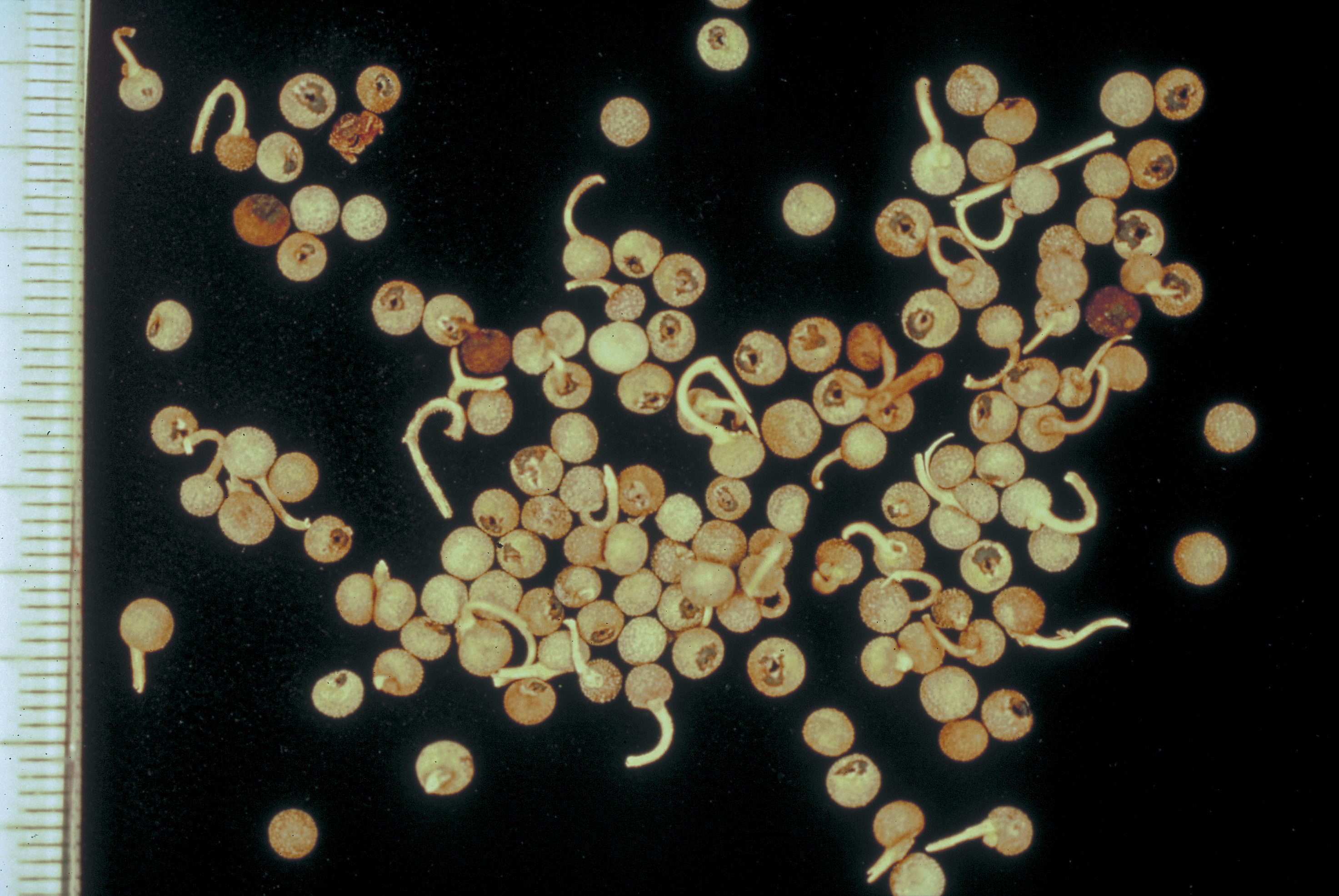
Seeds
- each flower forms a pair of seeds that separate when mature
- globular, 2 to 3 millimetres in diameter
- light to dark brown when dry, with on a hooked stem
- rough surface, with tiny warty bumps.

We need to find and eradicate three-horned bedstraw plants that exist in WA. Search (monitor) suspect paddocks, report suspect finds, and carry out prescribed control measures.
Monitoring
Three-horned bedstraw is easy to recognise among crop and pasture plants because of its distinctive appearance and feel, but hard to distinguish from other Galium species.
Who is likely to find it?
Cereal, pulse, and oilseed grain growers or agronomists in the South West Land Division.
When to find it?
Plants are most likely to be found from late winter to spring, when they are flowering, in any part of the South West Land Division where broadacre crops are grown.
Where to find it?
New infestations are likely to be identified in young crops between rows, before the crop canopy closes. It may also be found in pastures and fallow paddocks.
There is also a monitoring program to detect Bedstraw in grain. The monitoring program is implemented by CBH Group and funded by Grains, Seeds, and Hay Industry Funding Scheme.
Once bedstraw is confirmed, the department will help to determine the infested site/s and the best management options.

Report the presence of three-horned bedstraw before undertaking a control measure. Contact the department’s Bedstraw Project Manager (contact information under Contact us) for information about control methods.
Additional information
-
Three-horned bedstraw
-
Bedstraw Eradication Program 2024-25: Annual report to grain growers
Contact us
-
Martin AtwellBiosecurity Coordinator Industry Funding Schemes

